
Objects of Affection: Fieldwork

Passports (1940s–1980s)
Abel Wolman, chair of Sanitary Engineering from 1937 to 1961, consulted on the development of modern water and sewer systems in more than 50 countries.
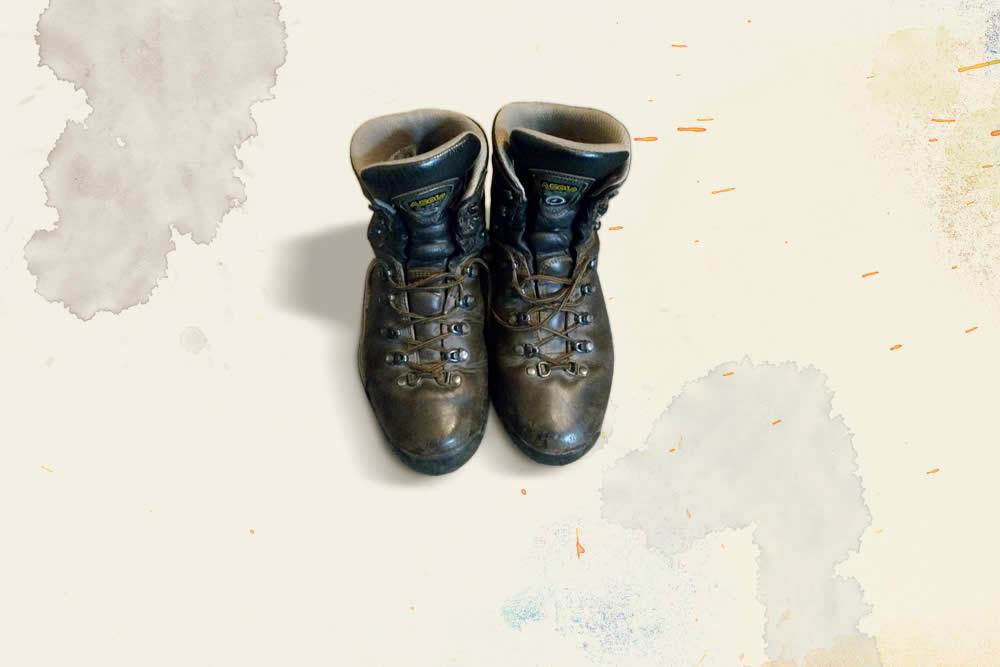

Boots (2015)
These boots were made for researchin'. Molecular Microbiology and Immunology Professor Doug Norris studies mosquitoes from Colombia to Zambia while wearing Asolos.
Zinc Packet (c. 1990s)
In Bangladesh, Peru, Zanzibar and elswhere, Robert Black, then chair of International Health, and colleagues showed that zinc can treat and prevent diarrhea, prevent pneumonia and reduce child mortality.
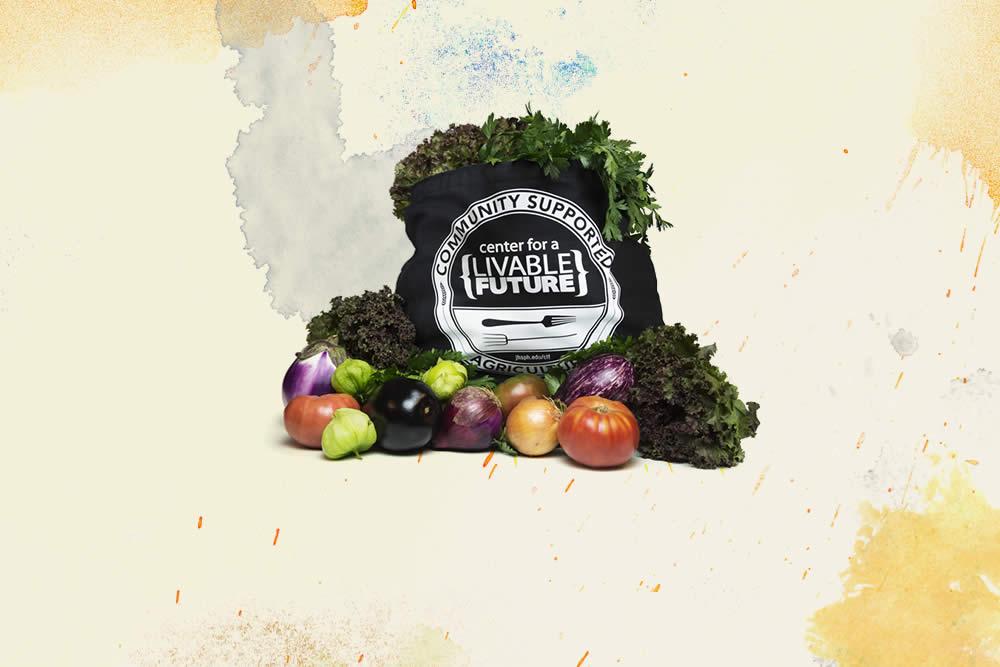

Cloth Produce Bag (2015)
Since 2007, the Center for a Livable Future and One Straw Farm have delivered fresh local produce to students and staff. Photo Credit: Michael Milli

Lapel Pin (c. 1960)
Alexander Langmuir, MD, MPH '40, and officers in the Epidemic Intelligence Service (which he founded at CDC) proudly wore lapel pins to symbolize the tradition of "shoeleather epidemiology."

Serviceman's Condoms (c. 1945)
During World War II, Thomas Tumer, chair of Bacteriology, directed the U.S. Army's venereal disease control program. He initiated an education blitz and led the distribution of up to 50 million condoms per month—to great success.
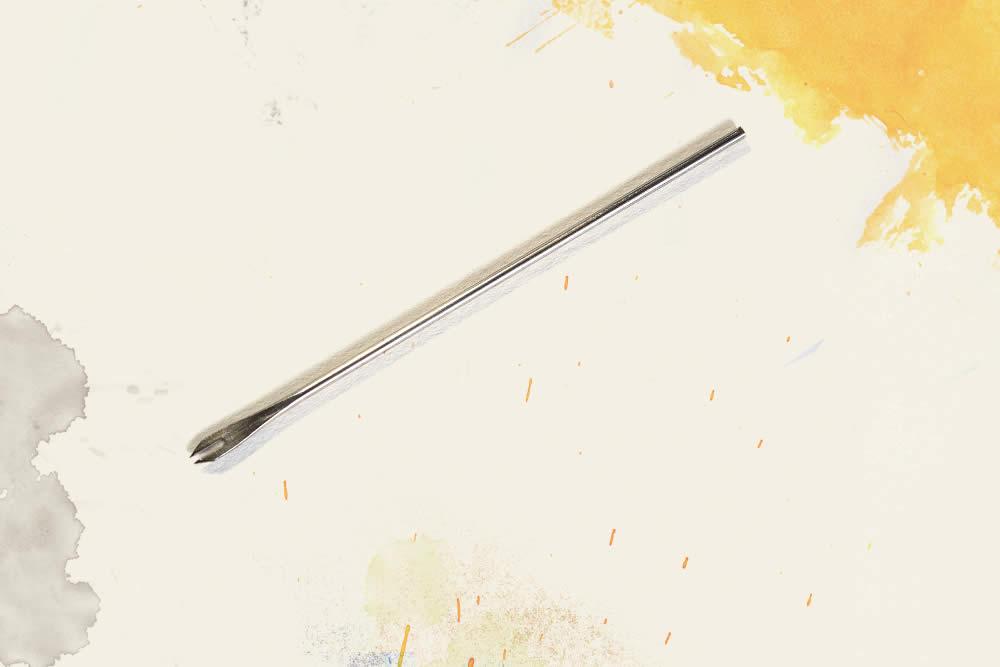

Bifurcated Needle (c. 1966)
The bifurcated needle was essential to the success of the WHO smallpox eradication campaign, directed by Dean Emeritus D.A. Henderson, MD, MPH '60. It was cheap, easy to use, required less vaccine and could be boiled and reused hundreds of times.

Notes on the Alma Ata Declaration (1978)
International Health chair Carl Taylor served as WHO's primary consultant on the historic Alma Ata Declaration on health care, adopted in 1978.